Install Satellite on RHEL8: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
=LINKS= | =LINKS= | ||
* https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_satellite/6.13/pdf/installing_satellite_server_in_a_connected_network_environment/red_hat_satellite-6.13-installing_satellite_server_in_a_connected_network_environment-en-us.pdf | * https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_satellite/6.13/pdf/installing_satellite_server_in_a_connected_network_environment/red_hat_satellite-6.13-installing_satellite_server_in_a_connected_network_environment-en-us.pdf | ||
* https://access.redhat.com/solutions/3382781 | |||
=OUTSIDE CONNECTIVITY NEEDS= | =OUTSIDE CONNECTIVITY NEEDS= | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
* https://cert-api.access.redhat.com | * https://cert-api.access.redhat.com | ||
=Install= | =Install= | ||
Revision as of 11:41, 14 June 2023
WIP, DO NOT USE!
VM SETUP
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8
- CPU: min 4
- MEM: min 20G
- DISK:
- / 10 GB -> 50 GB
- /var/log 10 MB -> 10 GB
- /var/lib/pgsql 100 MB -> 20 GB
- /var/lib/pulp 1 MB -> 300 GB
- /var/lib/qpidd ~2MB per managed host
LINKS
- https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_satellite/6.13/pdf/installing_satellite_server_in_a_connected_network_environment/red_hat_satellite-6.13-installing_satellite_server_in_a_connected_network_environment-en-us.pdf
- https://access.redhat.com/solutions/3382781
OUTSIDE CONNECTIVITY NEEDS
default
If using Insights
Install
subscription-manager register dnf -y install firewalld systemctl enable firewalld --now firewall-cmd \ --add-port="80/tcp" --add-port="443/tcp" \ --add-port="5647/tcp" \ --add-port="8000/tcp" --add-port="9090/tcp" \ --add-port="8140/tcp" \ #--add-port="53/udp" --add-port="53/tcp" \ #--add-port="67/udp" \ #--add-port="69/udp" firewall-cmd \ --add-port="80/tcp" --add-port="443/tcp" \ --add-port="5647/tcp" \ --add-port="8000/tcp" --add-port="9090/tcp" \ --add-port="8140/tcp" \ #--add-port="53/udp" --add-port="53/tcp" \ #--add-port="67/udp" \ #--add-port="69/udp" \ firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent firewall-cmd --list-all #ports: 80/tcp 443/tcp 5647/tcp 8000/tcp 9090/tcp 8140/tcp ping -c1 localhost ping -c1 `hostname -f` hostnamectl set-hostname `hostname -f` hostnamectl dnf -y install https://yum.theforeman.org/releases/3.5/el8/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm dnf -y install https://yum.theforeman.org/katello/4.7/katello/el8/x86_64/katello-repos-latest.rpm dnf -y install https://yum.puppet.com/puppet7-release-el-8.noarch.rpm dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools dnf module enable katello:el8 pulpcore:el8 dnf clean all dnf makecache dnf -y upgrade yum -y install chrony systemctl start chronyd systemctl enable chronyd chronyc sources reboot
Setup Foreman
foreman-installer --scenario katello --foreman-initial-organization "BITBULL" --foreman-initial-location "Verwaltung" --foreman-initial-admin-username admin --foreman-initial-admin-password admin --enable-foreman-cli-ansible --enable-foreman-cli --enable-foreman-cli-katello --enable-foreman-plugin-ansible --enable-foreman-plugin-remote-execution --enable-foreman-plugin-remote-execution-cockpit --enable-foreman-plugin-statistics --enable-foreman-plugin-tasks # --skip-checks-i-know-better --tuning development
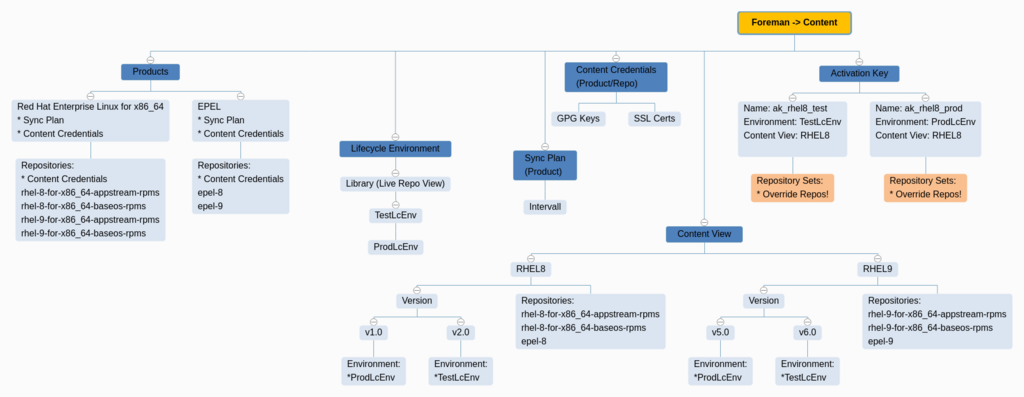
Foreman Content Management - Menu Overview
Manage Repos with Foreman
- https://opensource.com/article/21/9/centos-stream-foreman
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XsCi9Jy2lGs&t=3s
Create Content
- Content > Subscriptions
- Import Manifest
- Content > Red Hat Repositories
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 - AppStream (RPMs)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 - BaseOS (RPMs)
- Content > Sync Plans
- Create Sync Plan > Daily
- Content > Products > [X] Red Hat Enterprise Linux for x86_64
- Manage Sync Plan > Daily
- Sync Selected
- Content > Lifecycle Environment > Create
- TestLcEnv > ProdLcEnv
- Content > Content views > Create
- Name: cv_rhel8
- Solve dependencies: TRUE
- Content > Content views > cv_rhel8 > Publish new version
- Promote: TRUE
- Version: 1.0
- Env: TestLcEnv + ProdLcEnv
- Content > Activation Keys > Create
- Name: ak_rhel8_test
- Environment: TestLcEnv
- Content View: cv_rhel8
- Repository Sets: Disable all but needed
- Content > Activation Keys > Create
- Name: ak_rhel8_prod
- Environment: ProdLcEnv
- Content View: cv_rhel8
- Repository Sets: Disable all but needed
Patch Cycle Ideas Brainstorming
Prerequisites
- Daily Sync of all Foreman Libraries (Product upstream Repos)
- Working Repos as mentioned above
- Systems are grouped and registered in Lifecycle Environments
- TEST
- TEST-LATE
- PROD
- PROD-LATE
The meaning of "LATE" is to patch this systems later to avoid production issues (eg: half of the systems of a Cluster (DNS, Web, ...)
Patch Cycle
- All systems get patched at least every 4 weeks
- A Rundeck Job does update the Content Views on a regular base.
EXAMPLE: ---------------------------------- KW01 -> "Library" (daily sync) into "TEST" Content View as Version "KW01" KW02 -> Version "KW01" into "TEST-LATE" Content View KW03 -> Version "KW01" into "PROD" Content View KW04 -> Version "KW01" into "PROD-LATE" Content View KW05 -> "Library" (daily sync) into "TEST" Content View as Version "KW05" KW06 -> Version "KW05" into "TEST-LATE" Content View KW07 -> Version "KW05" into "PROD" Content View KW08 -> Version "KW05" into "PROD-LATE" Content View ...
Emergency Patching
Due security needs, it may be necessary to apply patches immediatly. For that, you have several options
Add Packages to Conent View
- Create a custom Repository eg. "Rocky9 Custom"
- Add RPMS, which are newer and needed for emergency patching to this repo
- They get applied with Ansible on a daily base during patch cycle
- Once they get obsolete (regular Repo gets updated) you can purge them out of the repo
Update Conent View
Easiest way to update repos but may apply more updates than needed for security reason
- Needs to pause the automated "Content View" update in Rundeck
Manual Update
Manually Update custom packages with yum/dnf on affected systems
- least prefered, due missing overview